Get Healthy!
Results for search "Neurology".
22 Dec
Doctors Reconnect 2-Year-Old’s Head to His Spine — Giving His Family a Holiday Miracle
After a devastating crash severed his spine, two-year-old Oliver Staub was not expected to survive. Groundbreaking surgeries at the University of Chicago Medicine helped him begin breathing and moving again, defying all odds.
19 Aug
New Concerns About the Use of Acetaminophen During Pregnancy
A new study finds prenatal exposure to acetaminophen may increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder and ADHD.
05 Mar
Sleep Apnea May Increase the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease, Preliminary New Study Finds
Patients with obstructive sleep apnea may have higher odds of developing Parkinson’s disease, but researchers say early CPAP treatment may lower the risk.
Health News Results - 679
FRIDAY, Feb. 20, 2026 (HealthDay News) — For years, families of athletes and military veterans have watched loved ones slip into memory loss, suspecting the culprit was a lifetime of blows to the head.
Now, a major study from the Boston University CTE Center provides the data to back those suspicions: Advanced chronic traumatic encephalopathy (C...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 20, 2026
- |
- Full Page
WEDNESDAY, Feb. 11, 2026 (HealthDay News) — What does it take to make others behave less selfishly and put others’ needs before their own?
Electrical zaps to the brain can do the trick, a new study shows.
Stimulating two brain areas increased people’s ability to behave altruistically, researchers reported Feb. 10 in the journal
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 11, 2026
- |
- Full Page
FRIDAY, Feb. 6, 2026 (HealthDay News) — Even before they can crawl or speak, infants are essentially "wired" for music.
A new study reveals that humans enter the world with a built-in ability to anticipate musical beats, though the capacity to track a melody takes a bit more practice and time to develop.
The research, published Feb. 5 in P...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- February 6, 2026
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, Jan. 22, 2026 (HealthDay News) — The human brain may understand spoken language in a way that is surprisingly similar to how artificial intelligence (AI) processes words, a new study suggests.
By tracking brain activity as people listened to a spoken story, researchers found that the brain builds meaning step by step, very similar to the way large AI language models do.
- I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter
- |
- January 22, 2026
- |
- Full Page
TUESDAY, Dec. 2, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Obesity might contribute to faster progression of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study says.
Some blood markers associated with Alzheimer’s increased nearly twice as fast among people with obesity ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- December 2, 2025
- |
- Full Page
TUESDAY, Dec. 2, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Ever wonder why you instinctively wince when you see physical harm come to a TV or movie character on screen?
There’s a scientific explanation for why we flinch when watching painful events, even though we know it’s not real, researchers reported Nov. 26 in the journal
MONDAY, Dec. 1, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Researchers say changes in folks' driving patterns could be an early signal of cognitive decline.
“We found that using a GPS data tracking device, we could more accurately determine who had developed cognitive issues than looking at just factors such as age, cognitive test scores and whether they had a genetic risk factor related to
- Ernie Mundell HealthDay Reporter
- |
- December 1, 2025
- |
- Full Page
TUESDAY, Nov. 25, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Add one more malady to the potential risks from untreated sleep apnea: Parkinson’s disease.
A new study involving 11 million U.S. veterans finds that a person’s odds of developing
THURSDAY, Nov. 20, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Use of head CT scans in U.S. emergency departments has more than doubled over the past 15 years, a new study says.
Nearly 16 million head CT scans were ordered by ERs in 2022, up from under 8 million in 2007, researchers reported Nov. 17 in the journal Neurology
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 20, 2025
- |
- Full Page
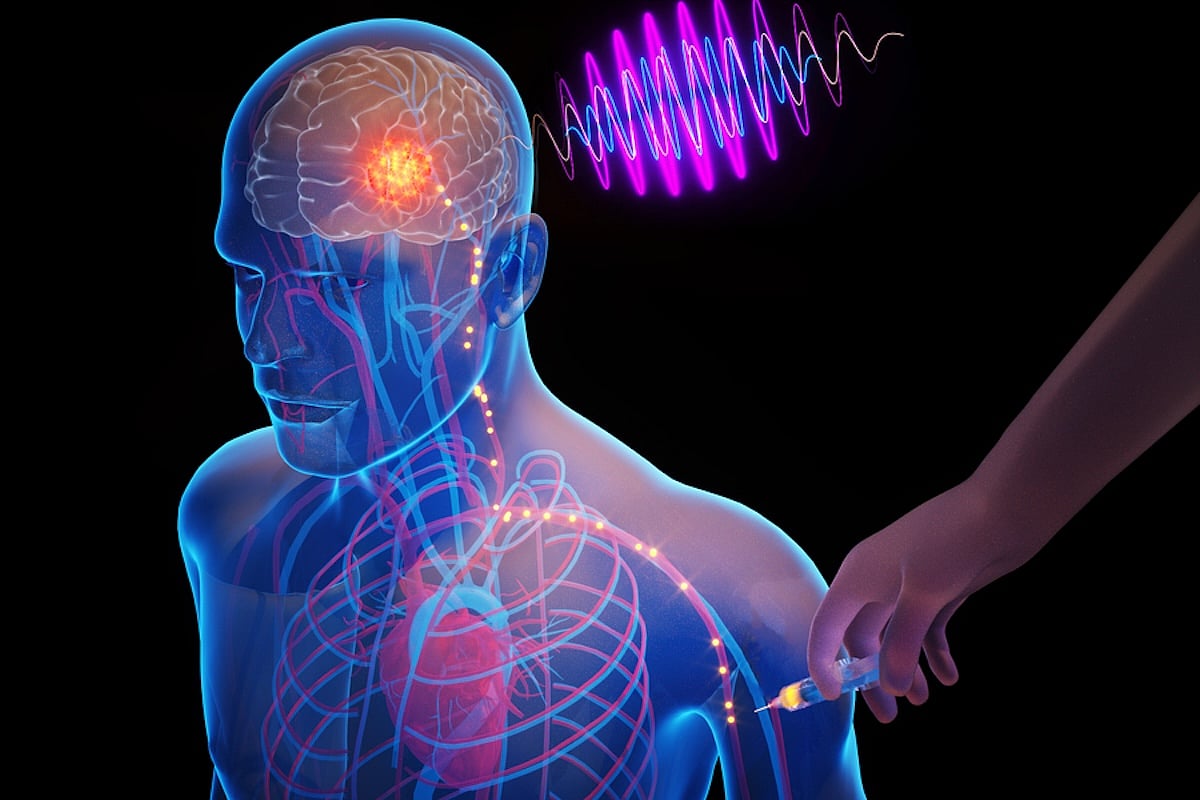
MONDAY, Nov. 10, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Imagine a brain implant that could be placed without surgically opening a person’s skull, but instead through a simple injection in the arm.
Massachusetts Intitute of Technology researchers are working on microscopic, wireless electronic chips that can travel through the bloodstream and self-implant in a targeted region...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- November 10, 2025
- |
- Full Page
TUESDAY, Oct. 28, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Folks who’ve suffered one or two concussions at some point shouldn’t worry about developing chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a new study has concluded.
CTE is more common in peo...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 28, 2025
- |
- Full Page
FRIDAY, Oct. 24, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Reality TV star, actress and mom Kim Kardashian, 45, disclosed in the season premiere of “The Kardashians” that a small aneurysm was detected in her brain.
An aneurysm occurs when a blood vessel wall weakens and stretches, creating a balloon or bubble. While aneurysms can appear anywhere, those in the brain, known as cerebral aneu...
- Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 24, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, Oct. 2, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Long-term exposure to a chemical used in metal degreasing and dry cleaning might increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease, a new study says.
Seniors living in places with the highest airborne levels of tr...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- October 2, 2025
- |
- Full Page
WEDNESDAY, Oct. 1, 2025 (HealthDay News) — In a move that surprised many in the scientific community, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded $50 million to 13 research projects focused on the complex and credible causes of autism.
The grants were announced just days after top administration officials, including Health Secretary
FRIDAY, Sept. 19, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Every movement we make, whether walking, speaking or even breathing, depends on the health of our muscles and nerves.
For people living with one of the more than 300 rare conditions known as neuromuscular diseases (NMDs), those everyday actions can become extraordinary challenges.
While these diseases such as muscular dystrophies, am...
- Brian Lin, PhD, Research Portfolio Director at the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 19, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, Sept. 18, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Nearly 4 out of 5 American neurologists prescribing multiple sclerosis (MS) drugs have received at least one payment from the pharmaceutical industry, a new study reports.
Those who prescribe larger amounts of MS drugs were more likely to have received payments, and those who got payments were more likely to prescribe the company’s d...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- September 18, 2025
- |
- Full Page
SATURDAY, Sept. 6, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Just like their human counterparts, cats may act cranky or confused and have trouble sleeping as they age.
They may even yowl more than usual at night.
These, researchers say, are dementia-like behaviors that may owe to an accumulation of plaques in their brain, just like those in people with
TUESDAY, Aug. 26, 2025 (HealthDay News) — It takes about a year for people with focal epilepsy to start finding some relief from anti-seizure medications, a new study says.
In all, 3 of 5 epilepsy patients (60%) do achieve freedom from seizures thanks to a drug regimen – but it ...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 26, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, Aug. 14, 2025 (HealthDay News) — It’s a time-honored and somewhat romantic tale: The young fighter who rises from poverty to make a name for themselves.
But reality might take some shine off such stories, a new study says.
Participants in combat sports like boxing or mixed martial arts who grew up in poor neighborhoods might be more likely to suffer brain chang...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 14, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, Aug. 7, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Researchers have debunked long-standing concerns that Tamiflu can cause neurological and psychiatric problems when given to influenza-stricken children.
For decades, doctors have debated whether the antiviral drug oseltamivir (Tamiflu) increases kids’ risk of seizures, mental problems an...
- Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter
- |
- August 7, 2025
- |
- Full Page
MONDAY, Aug. 4, 2025 (HealthDay News) — People with multiple sclerosis (MS) begin experiencing new health issues up to 15 years before the classic signs of the illness appear, Canadian research shows.
“MS can be difficult to recognize as many of the earliest signs — like fatigue, headache, pain and mental health concerns — can be quite general and easily mistaken f...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Ernie Mundell
- |
- August 4, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, July 31, 2025 (HealthDay News) — A life-threatening condition involving out-of-control brain swelling can occur in kids who are battling the flu, but it’s extremely rare.
A review of recent cases highlights the importance of quick diagnosis and aggressive treatment to saving the lives of kids with the condition, called influenza-associated acute necrotizing enc...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Ernie Mundell
- |
- July 31, 2025
- |
- Full Page
MONDAY, July 28, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Parkinson’s disease can dramatically affect a patient’s ability to walk, with “Parkinson’s gait” increasing their fall risk and reducing their ability to get around.
But deep brain ...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 28, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, July 24, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Insulin delivered by nasal spray might be a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, a new study says.
An insulin nasal spray effectively reached key memory regions in the brains of a small gro...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 24, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, July 10, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Folks who breathe in more air pollution have a higher risk of developing a common non-cancerous brain tumor, a new study says.
Several different types of air pollutants, including particle pollution and nitrogen dioxide, appear to increase risk of meningiomas — tumors that form in the layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal c...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 10, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, July 3, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Avid golfer Robert Knorr found he was no longer able to hit the links last year, due to neuropathy in his legs and feet.
The nerve pain got so bad that Knorr needed a cane — and sometimes a wheelchair — to get around.
But the 69-year-old retired oil company executive ha...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- July 3, 2025
- |
- Full Page
MONDAY, June 30, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Your address might influence your risk for dementia, a new study says.
People living in poor neighborhoods appear to be more likely to have biological risk factors for inflammation and Alzheimer’s diseas...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 30, 2025
- |
- Full Page
MONDAY, June 16, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Kids with multiple sclerosis (MS) age at an accelerated rate as the disease causes advanced wear and tear on their bodies, a new study says.
This accelerated aging extends into their teenage years, increasing their odds that MS-related disability and chronic disease will occur earlier in their lives, researchers reported June 9 in the journal...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 16, 2025
- |
- Full Page
FRIDAY, June 13, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Brain changes in sleepless teens could make them more likely to be impulsive and aggressive, a new study says.
Teenagers with less sleep had lower connectivity between the parts of the brain that play a critical role in decision making, self-reflection and information processing, researchers reported June 13 in the journal
THURSDAY, June 12, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Most folks tap away at their smartphone for fun, communication or information.
But such tapping may also help them track the progress of a rare degenerative brain disease, researchers say.
Five simple smartphone-measured tests of movement control can provide quick and regular insight into the motor function of someone with Huntington&...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- June 12, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, May 29, 2025 (HealthDay News) — Heart disease, strokes and diabetes contribute to many dementia cases in the United States, but the risk is not equal everywhere, a new study says.
Overall, more than a third (37%) of U.S. dementia cases are linked to eight co...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 29, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A brain wave decoder shows promise in using electrical stimulation to the spine to cue leg movement, researchers say.
The decoder could one day help restore mobility in people with spinal cord injuries.
Tests in 17 people without a spinal cord injury showed that the decoder could cue movement in their lower legs using spinal cord stimulation, researchers reported in the
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 20, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Knowing your risk for Alzheimer’s disease can provide peace of mind, but also might contribute to complacency regarding your overall health, a new study says.
People who underwent brain scans to learn their Alzheimer’s risk experienced less...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Sleep apnea could be costing you brain power and increasing your risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, a new study...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 8, 2025
- |
- Full Page
High school athletes with ADHD take longer to recover from a sport-related concussion, a new study says.
Those with a concussion took about 16% longer to return to the classroom and 17% longer to return to sports, compared to athletes without ADHD, researche...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- May 1, 2025
- |
- Full Page
THURSDAY, April 10, 2025 (HealthDay News) -- Having a father with Alzheimer’s disease could put you at risk for brain changes linked to the degenerative disorder, a new study says.
People whose fathers fell prey to Alzheimer’s had a greater spread of tau proteins in their brain, according to findings published in the journal
The first sign of seizures for Amanda Bradbury were auras in her vision that cropped up around age 19.
Then came frequent bouts of anxiety, struggling to maintain focus and follow conversations, forgetting things, and having difficulty speaking or even swallowing.
“One of the things that would happen before a seizure is I'd get an intense feeling of fear, which I now realize w...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 26, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A muscle-stimulating implant combined with a robotic exoskeleton can help restore movement in people paralyzed by a spinal cord injury, a new study says.
The spinal cord implant delivers well-timed electrical pulses to muscles, stimulating natural muscle activity coordinated with supportive robotic movements, researchers reported March 12 in the journal
Concussion damage could linger in an athlete’s brain for at least a year, long after they’ve rejoined their sport, a new study says.
Concussed college athletes had brain changes that remained visible in brain scans up to a year afte...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 13, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Sleep is a critical component for concussion recovery among kids, a new study reports.
Limiting naps during the day and getting about seven hours of sleep each night in the first week after a concussion appears to speed up recuperation, researc...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 11, 2025
- |
- Full Page
The number of people with Parkinson’s disease will more than double by 2050, driven by the aging of the global population, a new study suggests.
In all, 25.2 million people will be living with Parkinson’s by 2050, researchers project in The BMJ.
“An urgent need exists for future research to focu...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 7, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Hot flashes, night sweats and other symptoms of a difficult menopause could be early warning flags for dementia, a new study suggests.
Women who exhibit more menopause symptoms are more likely to develop early signs of dementia like decreased mental function and mil...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- March 6, 2025
- |
- Full Page
People hospitalized for a severe bout of COVID-19 are far from in the clear after they've recovered enough to return home, a new study says.
COVID hospital patients have an increased risk of death from any cause for at least two and a half years following their initial illness, researchers reported i...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 28, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Moving your body helps your brain, a new study suggests.
Folks who regularly exercise have better mental and brain health, researchers will report in early April at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology in San Diego and online.
Moderate to vigorous physical activity reduces risk of dementia, s...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 28, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A blood test can help doctors detect ALS, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and predict how the degenerative disease will progress in patients, a new study suggests.
People with ALS have three times higher blood levels of neurofilament light chain proteins, which are produced when nerve cells are injured or die, than people with other brain diseases, researchers reported Feb. 26 in the jo...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 27, 2025
- |
- Full Page
Artificial intelligence (AI) might help treat childhood epilepsy by detecting brain abnormalities that are causing kids’ seizures, a new study suggests.
The AI tool, called MELD Graph, found 64% of brain lesions linked to epilepsy that human radiologists had previously missed, researchers report in JAMA...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 27, 2025
- |
- Full Page
A baby’s seizure in a neonatal ICU could be a red flag for future risk of epilepsy.
Newborns who suffer seizures following birth are more likely to develop epilepsy in childhood and young adulthood, a
Mia Jack was stealing a glance backward when she lost control of the quadbike she’d been motoring around a family gathering.
Jack, then 12, flew over the handlebars and slammed headfirst into a tree.
“I was wearing a helmet at the time, but apparently my brain was like a jelly in a box that had been really badly shaken, and I was going to be in hospital for some ti...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Dennis Thompson
- |
- February 20, 2025
- |
- Full Page
From Mariah Carey and Jimi Hendrix to Michael Jackson, Ella Fitzgerald and Bing Crosby, a select group of famous musicians past and present have had have perfect pitch.
Now, a new study suggests that you can, too -- with proper training.
Absolute or perfect pitch is the ability to identify&nbs...
- HealthDay Reporter
- Denise Mann
- |
- February 18, 2025
- |
- Full Page